Targets
ChlaDUB1
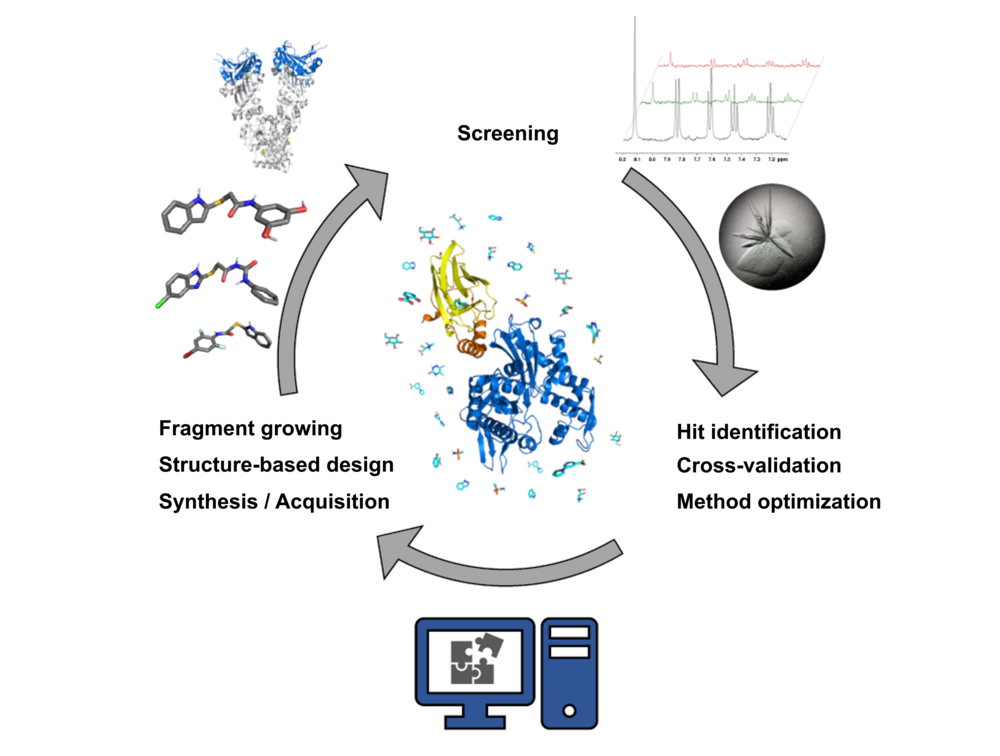
We work on the structure-based development of covalent inhibitors for the Chlamydia trachomatis deubiquitinase ChlaDUB1, a novel target for antibiotics to treat chlamydia infections.
Publications on this topic:
T. Zimmermann, J. Feng. S. Fischer, L. Janaína de Campos, F. Ramos Pinheiro, C. Sotriffer, M. Conda-Sheridan, M. Decker
Structural Optimization of Covalent Inhibitors for Deubiquitinase ChlaDUB1 of Chlamydia trachomatis as Antibiotic Agents
J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 5400–5425
T. Zimmermann, J. Feng, L. J. de Campos, L. A. Knight, J. Schlötzer, Y. A. Ramirez, K. Schwickert, M. Zehe, T. B. Adler, T. Schirmeister, C. Kisker, C. Sotriffer, M. Conda-Sheridan, M. Decker
Structure-Based Design and Synthesis of Covalent Inhibitors for Deubiquitinase and Acetyltransferase ChlaDUB1 of Chlamydia trachomatis
J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 10710–10742
Y. A. Ramirez, T. B. Adler, E. Altmann, T. Klemm, C. Tiesmeyer, F. Sauer, S. G. Kathman, A. V. Statsyuk, C. Sotriffer, C. Kisker
Structural Basis of Substrate Recognition and Covalent Inhibition of Cdu1 from Chlamydia trachomatis
ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 2014-2023
p97
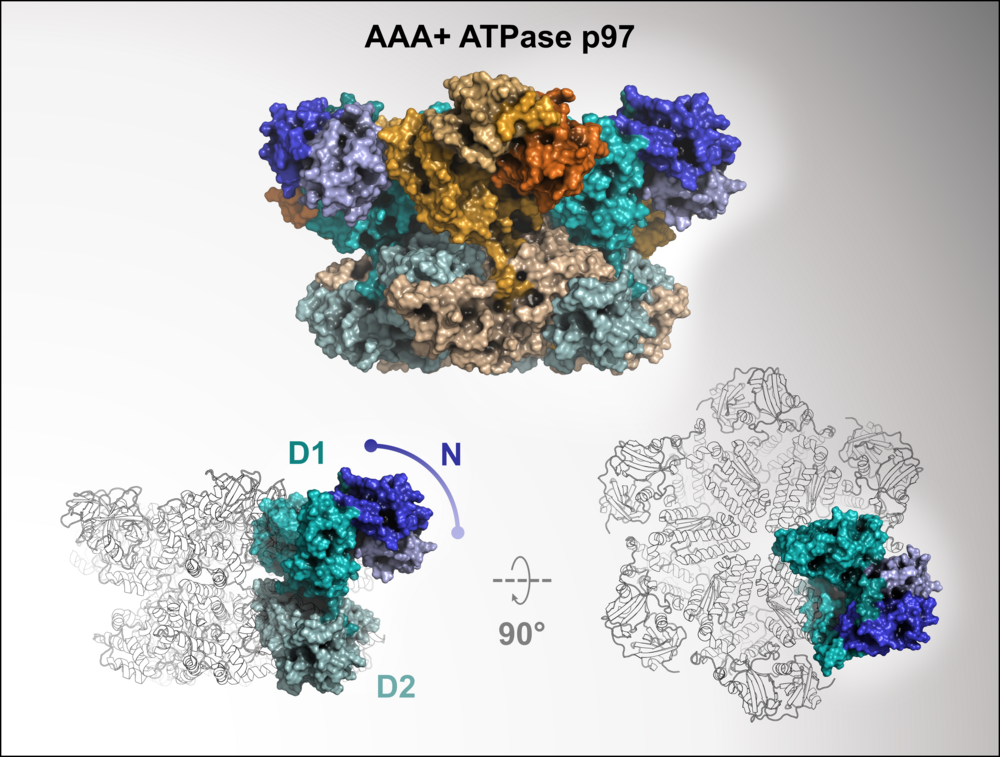
The AAA+ ATPase p97 is an essential protein with key roles in protein homeostasis and a possible target for cancer chemotherapy. We aim to develop inhibitors of cofactor binding to the N-domain to enable the selective targeting of specific p97 functions. Guided by molecular dynamics simulations, the binding sites of selected hits from a biolayer interferometry-based fragment screen were postulated and experimentally validated using protein- and ligand-based NMR techniques, as well as X-ray crystallography, ultimately resulting in the first structure of a small molecule in complex with the N-domain of p97.
Publications on this topic:
S. Bothe, P. Hänzelmann, S. Böhler, J. Kehrein, M. Zehe, C. Wiedemann, U. A. Hellmich, R. Brenk, H. Schindelin, C. Sotriffer
Fragment screening using biolayer interferometry reveals ligands targeting the SHP-motif binding site of the AAA+ ATPase p97
Commun. Chem. 2022, 5, 169
PGP
Phosphoglycolate phosphatase (PGP) is a prototypical metabolite repair enzyme in glycolysis that has emerged as a pharmacologically actionable target. With docking studies, virtual screening and MD simulations we are aim to understand the inhibition mode of currently known ligands and contribute to the development of optimized inhibitors.
Publications on this topic:
E. Jeanclos, J. Schlötzer, K. Hadamek, N. Yuan-Chen, M. Alwahsh, R. Hollmann, S. Fratz, D. Yesilyurt-Gerhards, T. Frankenbach, D. Engelmann, A. Keller, A. Kaestner, W. Schmitz, M. Neuenschwander, R. Hergenröder, C. Sotriffer, J. P. von Kries, H. Schindelin, A. Gohla
Glycolytic flux control by drugging phosphoglycolate phosphatase
Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6845
Hsp70
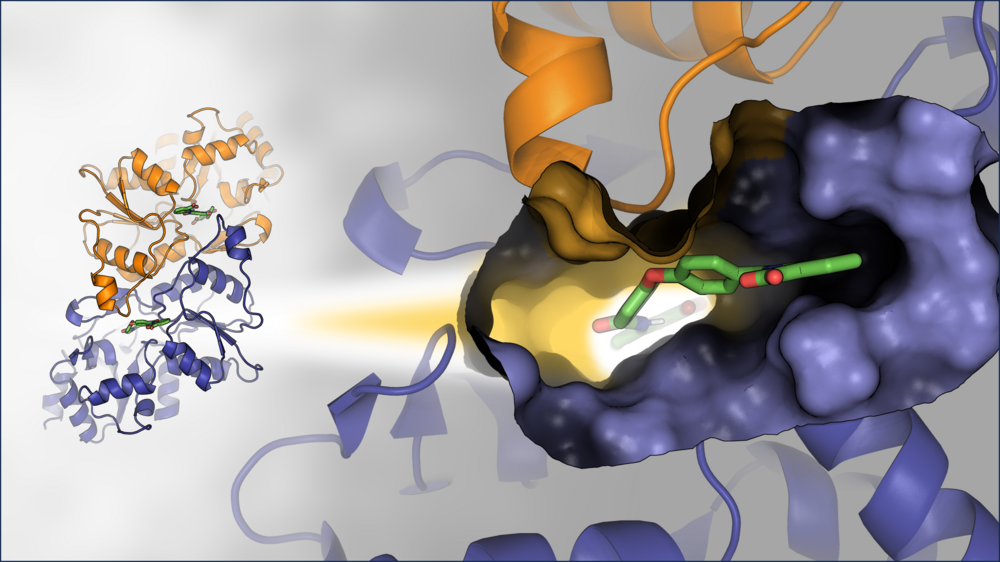
Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) isoforms are key players in the regulation of protein homeostasis and cell death pathways and are therefore attractive targets in cancer research. A fragment-based screening approach on a two-domain Hsp70 construct using NMR methods together with X-ray-crystallography and mixed-solvent MD simulations, resulted in hits on both domains of Hsp70. In particular, fragment binding in a deeply buried pocket at the substrate-binding domain could be detected. The corresponding site is known to be important for communication between the nucleotide-binding and substrate-binding domains of Hsp70 proteins and offers an interesting starting point for the development of a dual Hsp70/Hsp90 inhibitor.
Publications on this topic:
M. Zehe, J. Kehrein, C. Schollmayer, C. Plank, H. Kovacs, E. Merino Asumendi, U. Holzgrabe, C. Grimm, C. Sotriffer
Combined in-solution fragment screening and crystallographic binding-mode analysis with a two-domain Hsp70 construct
ACS Chem. Biol. 2024, 19, 392–406
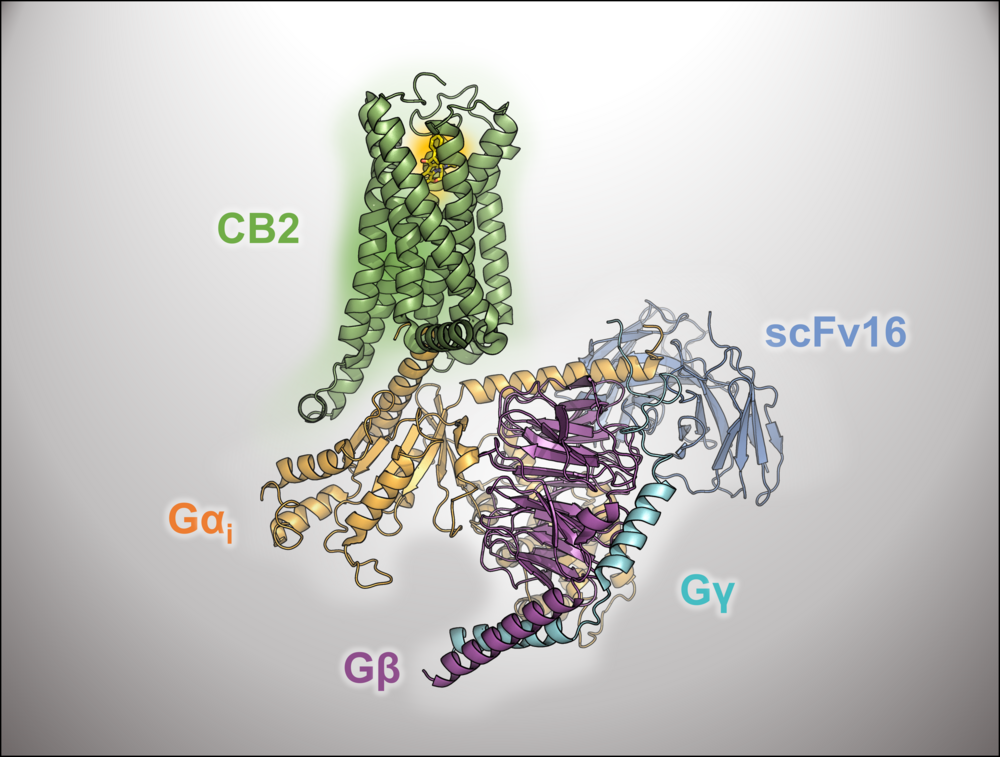
Cannabinoid receptor
In collaboration with the Decker group at the JMU Würzburg dualsteric and photoswitchable ligands for the cannabinoid receptors are computationally investigated to understand their binding modes and selectivity.
Publications on this topic:
A. Tutov, S. A. M. Steinmüller, Y. A. Ramírez, C. E. Jack, D. A. Rodríguez-Soacha, C. Sotriffer, J. N. Hislop, M. Decker
Bridging the binding sites: Dualsteric ligands for the cannabinoid 2 receptor (CB2R)
Adv. Therap. 2023, 6 (4), 2200260
D. A. Rodríguez-Soacha, S. A. M. Steinmüller, A. Işbilir, J. Fender, M. H. Deventer, Y. A. Ramírez, A. Tutov, C. Sotriffer, C. P. Stove, K. Lorenz, M. J. Lohse, J. N. Hislop, M. Decker
Development of an indole-amide-based photoswitchable cannabinoid receptor subtype 1 (CB1R) “cis-on” agonist
ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 2410-2435
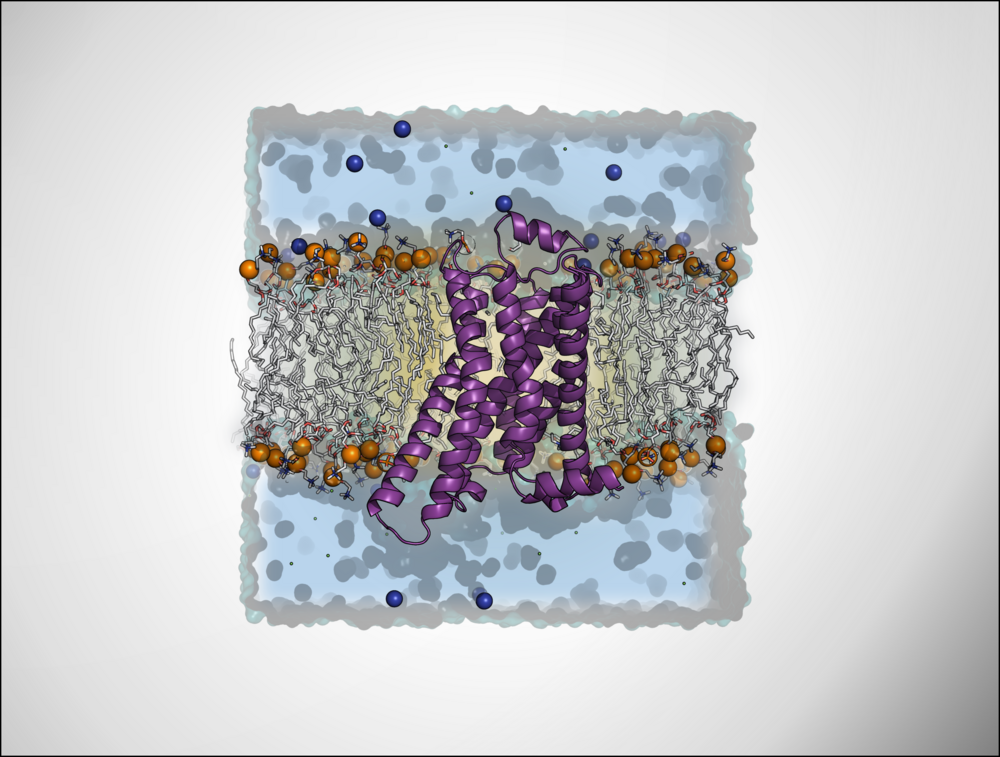
β-Adrenergic receptor
In collaboration with the Gmeiner group at the FAU-Erlangen we aim to develop bitopic ligands of the β-adrenergic receptor based on an understanding of the structural and functional properties of the orthosteric and the allosteric module and the impact of their ligation forming a bifunctional entity. The modules resulting from fragment-based virtual screening and chemical synthesis will be specifically functionalized and coupled. We work on diffusible as well as covalently binding ligands.
Further information on this topic: